Key Takeaways:
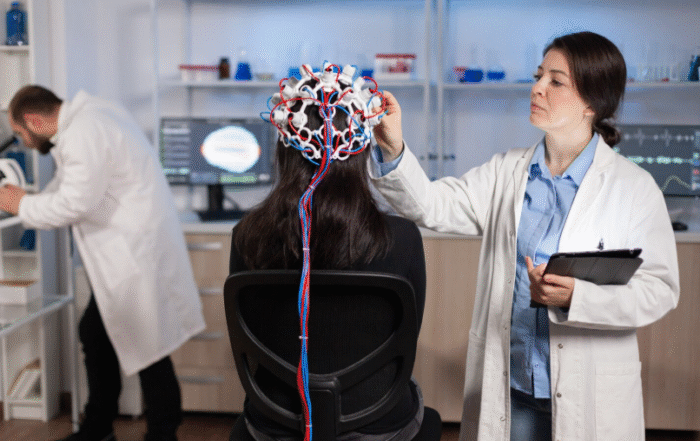
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): DBS has revolutionized treatment for movement disorders like Parkinson’s, tremor, dystonia, and drug-resistant epilepsy by modulating abnormal brain signals. Adaptive DBS devices such as Medtronic’s BrainSense enable real-time, personalized stimulation.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): TMS is a non-invasive therapy that uses magnetic pulses to stimulate brain regions, mainly for depression, migraines, and OCD. It has few side effects, is outpatient-friendly, and may help with chronic pain and PTSD.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): VNS sends electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, reducing seizures in epilepsy and aiding mood in treatment-resistant depression. It requires surgical implantation, but outcomes can be life-changing.
- Non-Invasive Cerebellar Stimulation:Targeting the cerebellum via TMS or tDCS may improve movement, balance, mood, and chronic pain, offering potential when conventional treatments fail.
- Optically-Generated Focused Ultrasound (OFUS): OFUS uses precise ultrasound to modulate the brain non-invasively, minimizing tissue impact and showing promise for neurological disorders.
- Regenerative Brain Cell Therapy:Therapies like NRTX-1001 aim to restore brain function by implanting specialized nerve cells, offering hope for conditions unresponsive to traditional treatments.
- Overall: Advances in non-drug neurological therapies offer more personalized, holistic options, expanding possibilities for patients with neurological disorders.
Over the past decade, non-pharmacological treatments for neurological disorders have rapidly gained traction among clinicians, researchers, and patients alike. As interest in holistic approaches and alternatives to medication grows, cutting-edge interventions are being developed to manage neurological symptoms more effectively. These diverse therapies offer promising outcomes for individuals looking to maintain their health without relying exclusively on pharmaceuticals. For those in the Rocky Mountain region, Colorado Integrated Neurology stands out as a regional authority in this evolving field.
Colorado Integrative Neurology in Boulder blends traditional and integrative neurology, using evidence-based non-drug therapies and medical expertise to serve patients statewide. Their focus on patient-centered care and innovative treatments makes them a top resource for alternative treatments. Advances in neurology now offer effective treatments with fewer side effects, aimed at improving quality of life. This article reviews recent non-drug therapies, brain stimulation, nerve modulation, and regenerative methods, showing how they are transforming neurological care across the U.S.
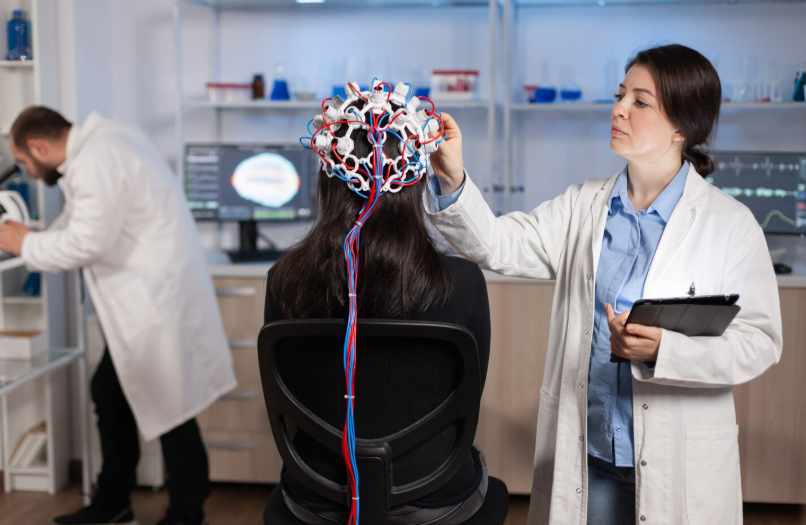
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) has significantly changed the management of certain movement disorders by implanting electrodes in specific brain regions to modulate abnormal electrical signals, thereby alleviating symptoms with fewer systemic side effects than medications. Initially developed as a therapy for Parkinson’s disease, DBS is now also employed for essential tremor, dystonia, and drug-resistant epilepsy. A notable advancement is the recent approval of adaptive DBS devices, such as Medtronic’s BrainSense, which offer real-time personalized stimulation that responds to the brain’s electrical activity and dynamically adjusts treatment. These innovations provide new hope for patients struggling to control their symptoms with medication alone.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation is a non-invasive treatment that leverages focused magnetic pulses to stimulate nerve cells in specific brain regions. Recognized and approved by the FDA, TMS is widely used to help patients with major depressive disorder, migraine headaches, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. The appeal lies in its safety profile and minimal side effects, making it suitable for individuals who have not responded well to medications.
Emerging research suggests additional benefits for TMS in treating chronic pain and post-traumatic stress disorder, potentially expanding its range of clinical applications in the coming years. Because TMS sessions do not require anesthesia and can be performed in an outpatient setting, it is an increasingly accessible choice for many patients.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
Vagus Nerve Stimulation utilizes small electrical impulses directed at the vagus nerve, which extends from the brainstem through the neck and into the body. This stimulation affects key brain regions involved in mood regulation and seizure activity. VNS is predominantly used to treat epilepsy, particularly forms that are resistant to traditional medications, as well as treatment-resistant depression.
Clinical studies show that VNS can meaningfully reduce seizure frequency and severity and may also support improved mood and cognitive outcomes. This approach requires surgical implantation of a device similar to a pacemaker, but once in place, it can be life-changing for many patients and their families.
Non-Invasive Cerebellar Stimulation
This emerging therapeutic approach focuses on stimulating the cerebellum, a region at the back of the brain critical for movement and balance. Using methods like TMS or transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), researchers are exploring its effectiveness in treating chronic pain syndromes, mood disorders, and enhancing recovery after stroke.
While non-invasive cerebellar stimulation shows potential, ongoing research is required to fully establish its clinical value. Early results indicate that such interventions may offer relief and functional improvement when conventional treatments fall short.
Optically-Generated Focused Ultrasound (OFUS)
OFUS represents a forward-thinking approach in brain stimulation. Rather than relying on electrodes or electromagnetic pulses, OFUS uses precisely targeted ultrasound waves to modulate specific areas of the brain. This method is completely non-invasive and highly precise, minimizing unintended effects on other brain tissue.
Preliminary studies highlight the promise of OFUS for neuromodulation, pointing to a future in which clinicians could treat neurological disorders without the need for surgery or implants. As technology advances, the hope is to see wider adoption of OFUS in clinical practice, further broadening the spectrum of non-drug neurological therapies.
Regenerative Brain Cell Therapy
Regenerative cell therapy, like NRTX-1001, aims to restore brain function by implanting specialized nerve cells into damaged areas, potentially reducing seizures and offering hope for previously intractable conditions. As research advances, these therapies could become crucial for patients unresponsive to current treatments, marking a significant shift in neurology.
Conclusion
The field of neurology is entering a transformative era with rising non-drug treatments like deep brain stimulation, transcranial magnetic stimulation, vagus nerve stimulation, non-invasive cerebellar stimulation, focused ultrasound, and regenerative brain cell therapy, offering more options. As these become more accessible, those with neurological disorders will benefit from personalized, holistic care. Clinics like Colorado Integrated Neurology highlight the importance of expert guidance and innovation, shaping neurological health in Colorado and beyond. For more on these advancements, sources like Nature offer in-depth research perspectives.
Key Takeaways: Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): DBS has revolutionized treatment [...]
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) addresses hormonal imbalances using compounds [...]
Sports medicine is a branch of healthcare dedicated to improving [...]
Chronic discomfort requires specialized medical intervention. Acute symptoms typically resolve [...]
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a chronic progressive condition that [...]
A successful outcome often starts well before the procedure itself, [...]
Missing teeth can affect your ability to chew and speak [...]
Refractive errors are very common, necessitating the use of eyeglasses [...]