A root canal is a dental procedure used to treat infection or damage within a tooth and prevent further complications. While the term often raises concerns for patients, modern techniques have made endodontic treatment safe, efficient, and comfortable. Here’s a closer look at what to expect during a root canal procedure:
Preparing for Treatment
Before the root canal procedure begins, the dentist will examine the painful tooth and the surrounding gums to identify the source of the problem. They will take X-rays to check the shape of the root canals and look for signs of infection in the surrounding bone. Once the assessment is complete, the dentist administers a local anesthetic to numb the tooth and the surrounding area. After the area is numb, the dentist places a small sheet of rubber, called a dental dam, around the tooth. This isolation technique keeps the tooth dry and clean and prevents saliva from entering the tooth during the process.
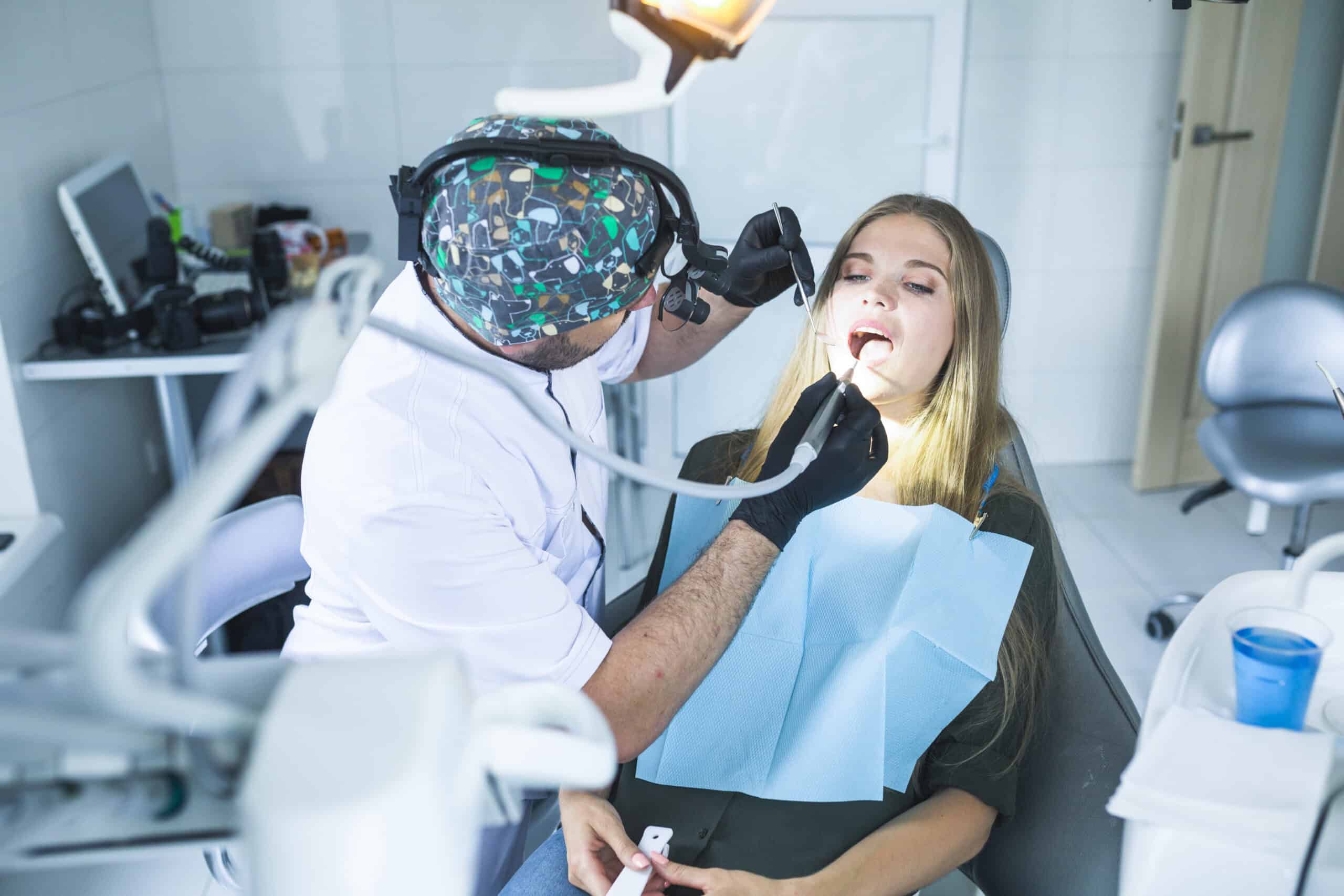
Performing the Root Canal
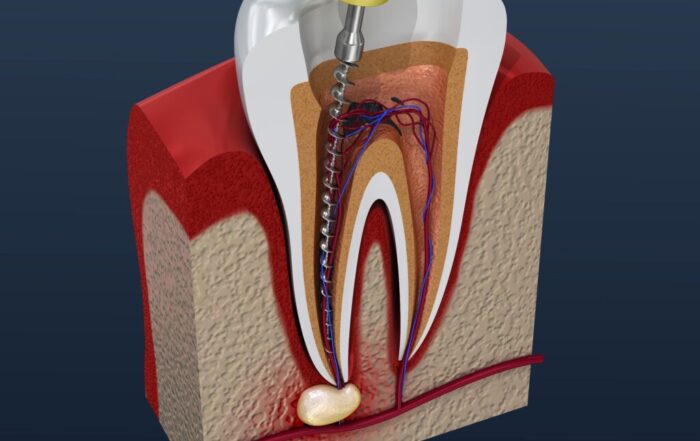
Once the tooth is prepared and isolated, the dentist proceeds with the core steps of the endodontic therapy. Here are the specific steps of the procedure:
- The dentist makes a small opening in the crown (top) of the tooth to access the pulp chamber.
- Very small dental instruments called files are used to remove the infected or inflamed pulp from the pulp chamber and canals.
- The dentist shapes the canals to prepare them for the filling material.
- Irrigation solutions are used to clean and disinfect the hollow canals, removing any remaining debris or bacteria.
- The canals are filled with a biocompatible material called gutta-percha.
- Adhesive cement is applied to seal the canals to prevent bacteria from entering the tooth again.
- A temporary filling is placed to close the access opening until a final restoration, such as a crown, is ready.
These steps remove the source of infection and protect the tooth’s interior from further damage.
Experiencing Sensations
Patients often worry about pain, but the local anesthetic makes the procedure painless. You may experience pressure or vibration during the procedure, but sharp pain is not part of the experience. If you feel any discomfort, you can signal the dentist to stop and administer more anesthetic.
After the appointment, the numbness from the anesthetic will last for a few hours. You should avoid eating a heavy meal until the numbness wears off to prevent biting your cheek or tongue. Once the anesthesia fades, you may experience some sensitivity or mild soreness in the area. This is a normal response, as the tissue surrounding the tooth heals from inflammation. Over-the-counter pain relievers are usually sufficient to manage this temporary discomfort. If you experience severe pain or visible swelling, you should contact your dentist immediately.
Recovering After Treatment
A tooth that has undergone root canal therapy can become brittle over time because there is no longer a pulp to supply it with nutrients. You should follow these guidelines to support a smooth recovery:
- Avoid chewing or biting down on the treated tooth until the final crown or restoration is in place.
- Brush and floss your teeth daily to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent new infections.
- Make sure you attend your follow-up appointment to have the permanent restoration placed.
Following these instructions and the post-treatment instructions from your dentist helps the tooth heal properly.
Schedule Your Root Canal Appointment
Root canal therapy is a reliable procedure that saves damaged teeth and eliminates pain. Understanding the steps involved prepares you for the appointment and procedure. If you are experiencing symptoms of an infected tooth, contact a qualified dentist in your area today to schedule your root canal appointment.
Therapy is a structured medical treatment designed to manage various [...]
Cataracts cause clouding in the lens of the eye, and [...]
Epidural steroid injections are a medical treatment for specific types [...]
Untreated OCD (Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder) at work is rarely obvious in [...]
The digestive system is responsible for converting food into the [...]
Custom orthotics offer a scientifically-backed solution for addressing biomechanical inefficiencies [...]
Substance abuse disorders remain a major concern, impacting individuals, families, [...]
General dentists manage a wide spectrum of oral health needs [...]