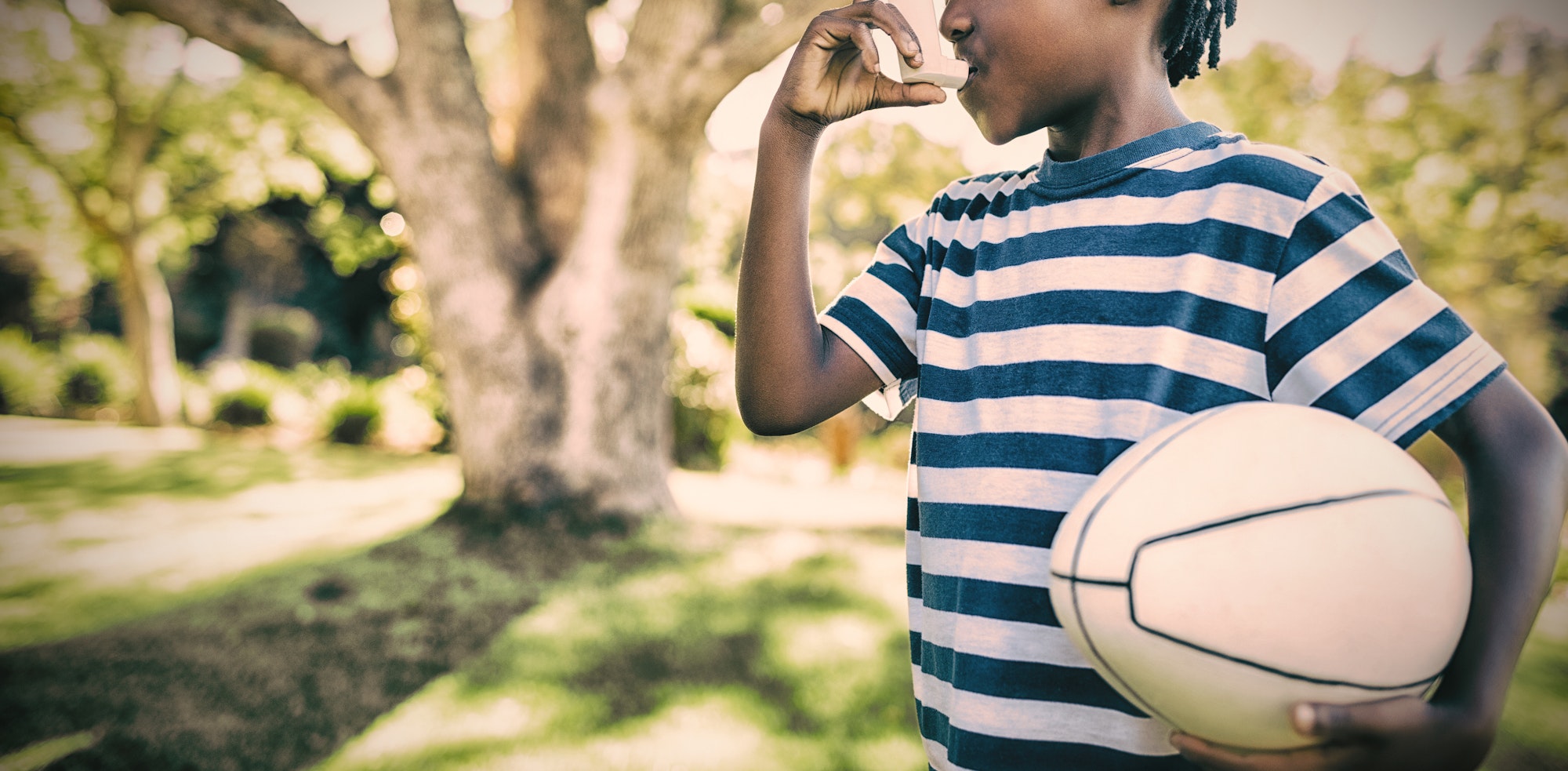
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that involves inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs. This may cause recurring periods of wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and coughing. The severity of asthma varies from person to person, but for many, it requires ongoing management to control symptoms and prevent serious attacks. Developing an effective management strategy with a healthcare provider is fundamental to maintaining lung health. Here’s information on three standard asthma management techniques:
Avoiding Triggers
A key component of asthma management is the identification and avoidance of specific triggers that can induce symptoms. Triggers are substances or conditions that irritate the airways, and they differ significantly among individuals. Some common environmental triggers include airborne substances such as:
- Pollen
- Dust Mites
- Mold Spores
- Pet Dander
- Cockroach Particles and Waste
Other potential asthmatic triggers include respiratory infections, physical activity, cold air, and air pollutants.
Once you and your healthcare provider identify your specific triggers, you can develop strategies to minimize exposure. This might involve checking daily pollen counts and staying indoors on high-pollen days, or using air purifiers to reduce indoor allergens. Keeping a journal of your symptoms helps you pinpoint patterns and identify triggers, which allows for more effective avoidance and better overall control of your condition.
Having Medication Accessible
Consistent and correct use of prescribed medications is a fundamental part of managing asthma. These medications work to reduce airway inflammation and prevent symptoms. There are two general categories of asthmatic medications: quick-relief and long-term use.
Quick-Relief Inhalers
Often called rescue inhalers, these medications provide rapid, short-term relief of asthma symptoms during an attack. They work by quickly relaxing the tightened muscles around the airways, allowing you to breathe more easily. It is imperative to carry a quick-relief inhaler at all times, as a delay in treatment during an asthma flare-up can be serious.
Long-Term Control Medications
These medications are taken daily on a long-term basis to control chronic symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. They reduce airway inflammation and are a fundamental treatment for many people with persistent asthma. Unlike quick-relief inhalers, they do not provide immediate relief, but their consistent use is key to managing the underlying condition.
Emergency Action Plans
An asthma action plan is a written document you develop with your doctor that details your daily treatment and explains how to handle an asthma attack. This plan outlines which medications to take, how to identify worsening symptoms, and when to seek emergency medical attention. Having a clear, accessible plan provides a guide for you and others, enabling proper management steps when symptoms escalate.
Adjusting Your Home Environment
Making targeted changes to your home can significantly reduce exposure to indoor asthma triggers. Simple modifications help create a healthier living space and contribute to better asthma control. Focus on areas where allergens commonly accumulate, such as bedrooms and living areas.
Using dust-proof covers on mattresses and pillows helps limit exposure to dust mites, and washing bedding weekly helps eliminate them. Regular vacuuming with a vacuum cleaner that has a HEPA filter can trap small particles that might otherwise be recirculated into the air. Maintaining low indoor humidity may also discourage the growth of mold and reduce the presence of other allergens. For individuals sensitive to pet dander, keeping pets out of the bedroom can help create an allergen-free zone for sleeping.
Schedule an Asthma Appointment
An effective asthma management approach often includes identifying and avoiding triggers, using medication as prescribed, and modifying personal environments. Asthma management is an ongoing process that also requires regular consultation with a healthcare professional. Your doctor can help you create a personalized treatment plan, adjust medications as needed, and provide guidance on managing your specific symptoms and triggers. If you are experiencing difficulty breathing, contact an immunology specialist for personalized medical guidance.
Menopause marks the permanent end of menstrual periods and fertility, [...]
Mental healthcare services focus on improving emotional and psychological well-being. [...]
Geriatric healthcare focuses on promoting and managing the health of [...]
A retinal detachment diagnosis can be concerning. If this has [...]
Musculoskeletal chest pain refers to discomfort originating in the muscles, [...]
Prenatal care is the ongoing medical support provided during pregnancy [...]
An oral surgeon, or a maxillofacial surgeon, is a dental [...]
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end [...]